See also
Procedural sedation
Intravenous access - Peripheral
Peripheral intravenous (IV) device management
Key points
- Early identification and appropriate management of extravasation is crucial in order to prevent serious adverse outcomes
- Do not flush the intravenous device following extravasation
- Neurovascular compromise second to extravasation is a surgical emergency and requires prompt recognition and management
Background
- Extravasation refers to the leaking of a fluid or medication into extravascular tissue from a peripheral intravenous (IV) cannula or central venous access device (CVAD) with potential to cause short or long term tissue damage
- Risk factors for extravasation injuries include:
- neonates
- using small or fragile veins
- insertion of IV lines across joints
- poorly secured IV lines
- patient sedation, paralysis or inactivity
- paraesthesia or neuropathy
- impaired neurocognition or communication
- Severity of extravasation injury depends on the volume infused into the tissue and the drug properties (pH, osmolarity and pharmacological action of the drug)
- Some drugs cause significant local tissue damage (erythema, blistering, ulceration or necrosis) when they enter the extravascular space
- Large volumes can cause nerve compression and compartment syndrome
- Prompt recognition and management can prevent the need for surgical intervention, permanent scarring or loss of function
Assessment
- Assessment of a peripheral IV cannula should occur at the time of infusing a drug, or frequently if there is an ongoing infusion
- Assessment of extravasation severity is not limited to a single point in time. Intervention should be made whenever the threshold defined below is met
- Onset of signs and symptoms may occur many hours after extravasation occurs
- All extravasation injuries should be photographed, and images saved to the child’s medical record
- Ask about pain, burning or stinging, or complete a
pain assessment if child is non-verbal
- Peripheral IV line site assessment should involve visualising, palpating and comparing the site with the opposite limb/other side of the body
Examination
Signs and symptoms of extravasation may include:
- Sudden change in infusion pressure or speed when infusing a drug
- Leakage of fluid from insertion site
- Changes in sensation surrounding or distal to the site eg pain, burning, or tingling. Use a pain scale where appropriate
- Swelling at the IV line site, along the vein pathway or down the limb
- Skin changes including erythema, induration, blistering, pallor or blanching
- Absence or decrease of capillary return
- Attempt to distinguish extravasation from venous irritation (symptoms often coincide with start of infusion) or local flare reaction (itch and red blotching along the vein)
- Diluting or slowing infusion may assist symptoms of venous irritation or local flare reaction
Assessment of severity
- Volume of fluid infused
- Type of drugs and/or fluids delivered in past 2 hours or since the last site assessment (whichever is longer)
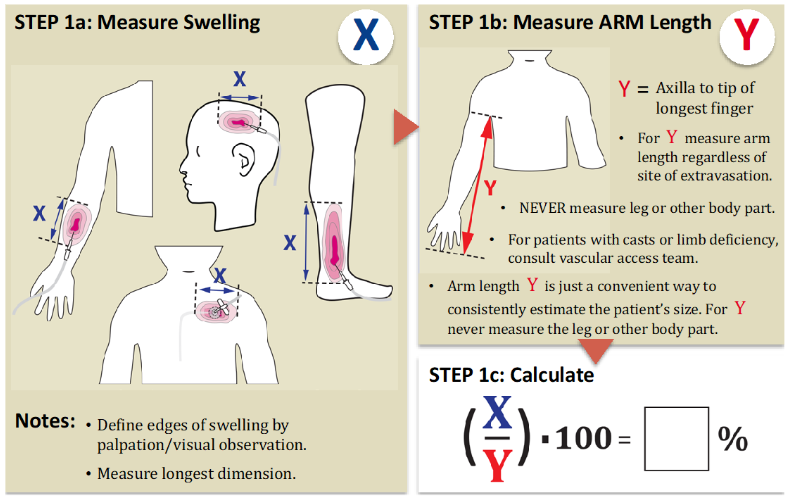
- Size of swelling: see below for estimation of percentage of swelling
- Signs of neurovascular compromise
- capillary refill at the site of the extravasation
- capillary refill time distal to the extravasation
- presence of distal pulses
- Signs of compartment syndrome: severe pain especially with passive flexion of affected muscle compartment, tightness, pallor, paraesthesia, weakness or paralysis
- Signs of impending tissue ischaemia: blanched skin, an area with central grey/black discolouration, numbness, prolonged capillary refill time
STEP 1: Assess degree of swelling
Estimate volume infused into the tissues
STEP 2: Stratify drug and fluid risk
List of medications based on risk profile:
Green
Low risk |
Yellow
Intermediate risk |
Red
High risk |
|
Aminophylline
Amphotericin B liposomal
Ampicillin
Benzylpenicillin
Cefazolin
Cefotaxime
Ceftazidime
Ceftriaxone
Cefuroxime
Clindamycin
Glucose
<10%
Fentanyl
Fosphenytoin
Furosemide
Gentamicin
Heparin
Imipenem/Cilastatin
Iron infusion
IVIG
Lactated ringers
Magnesium sulfate
Meropenem
Methylprednisolone
Sodium chloride 0.9%
Sodium chloride 0.45%
Pentamidine
Piperacillin/Tazobactam
Tobramycin |
Acetazolamide
Alteplase
Amikacin
Arginine
Ciprofloxacin
Glucose 10 to ≤12.5%
Dantrolene
Diazepam
Digoxin
Etomidate
Erythromycin
Flucloxacillin
Ganciclovir
Lorazepam
Midazolam
Morphine
Mycophenolate
Nitroglycerine
Ondansetron
Phenobarbital
Phenytoin
Propofol
Radiographic contrasts
Sulfamethoxazole/
Trimethoprim
Thiopental sodium
Any medication containing propylene glycol |
Aciclovir
Alprostadil
Amiodarone
Caffeine citrate
Calcium (all salt forms)
Cytotoxic medications
Glucose >12.5%
Doxycycline
Epoprostenol
Esmolol
Foscarnet
Mannitol
Metronidazole
Nitroprusside
Promethazine
Potassium chloride >40 mmol/L
Sodium bicarbonate ≥3%
Sodium chloride ≥3%
Sodium valproate
Total parental nutrition (TPN)
Vancomycin Vasoactive medication (eg adrenaline, dobutamine, dopamine, milrinone, noradrenaline, phenylephrine, prostaglandins, vasopressin) |
Note: This list is not exhaustive. If a medication does not appear on this list, contact local pharmacist for advice. Extravasation of any medication may cause serious harm, ischaemia or compartment syndrome.
Management
Investigations
No investigations are required
Treatment
- Stop infusion
- Do not remove IV line
- Elevate affected limb if possible. Do not apply pressure
- Do not flush the line
- Attempt aspiration of remaining drug from IV line with a small syringe
- Administer
pain relief if required
- Assess extent of swelling and type of drug/fluid (above), and use table below to guide management
- A warm compress may be used to disperse the drug over a larger area eg extravasated glucose, antibiotics, TPN, concentrated glucose solutions and electrolytes
- A cold compress may be used to limit distribution of the drug eg extravasated IV contrast. Do not use for extravasation of vasoactive medications as this causes further vasoconstriction and ischaemia
- Mark and photograph the whole area of extravasation injury
Note: compromise to the neurovascular status of the limb or suspected compartment syndrome is a surgical emergency and requires immediate referral to plastic/relevant surgical team
Management
| % Swelling
and infusate |
Action |
|
Any extravasation of
Vasoactive medication
from the Red infusate list
adrenaline, dopamine, noradrenaline and related medication |
Review immediately
Prepare for treatment with Phentolamine (below)
Do not use ice/cold compress as this will cause further vasoconstriction |
|
Extravasation ≥30%
AND
Red list infusate |
Review within 30 minutes
Prepare for washout procedure (below)
Washout procedure should be performed as soon as possible and within 12 hours
Notify plastic/local surgery team if the washout procedure may need to be performed in the operating theatre
Consider treatment with Hyaluronidase (see dose below) |
|
Extravasation <30%
AND
Red list infusate |
Review within 30 minutes
Hourly observation and reassessment of the injury for 48 hours
Notify plastic/relevant surgical team in hours
Washout procedure only required if progressing towards ≥30% swelling or evidence of impending tissue ischaemia (above)
Consider treatment with Hyaluronidase (see dose below) |
|
Extravasation ≥30%
AND
Yellow or Green list infusate |
Review within 30 minutes
Hourly observation and reassessment of the injury for 48 hours
Treatment not usually required
A washout procedure is required if there is impending tissue ischaemia or if swelling >60%
Discuss with a plastic/relevant surgical team if worsening, to determine whether treatment is needed
Consider treatment with Hyaluronidase (see dose below) |
|
Extravasation <30%
AND
Yellow or Green list infusate |
Non-urgent review
4 hourly observation and reassessment of the injury for 24 hours
Treatment not usually required but may be indicated if swelling increasing or evidence of impending tissue ischaemia
A washout procedure is indicated if there is impending tissue ischaemia |
Note: Local guidelines may differ, please see local policy where appropriate
Antidotes
Phentolamine
- alpha-adrenergic receptor antagonist
- Can be used to counter the effects of vasoconstriction and ischaemia in the event of vasopressor extravasation
- Preparation:
- 5 mg made up to 10 mL with 0.9% sodium chloride
(1 mL = 0.5 mg Phentolamine)
- Instructions:
- Inject in 4-5 small aliquots intradermally across the site of injury
- Dose 0.1-0.2 mg/kg to a maximum dose of 5 mg
- Ideally injection is administered as soon as possible, but may be used up to 12 hours following injury
Hyaluronidase
- Hydrolyses hyaluronic acid and allows dispersion of extravasated fluid
- May be used to reduce necrosis in severe extravasation
- Preparation:
- dissolve hyaluronidase powder (1500 IU) in 1 mL of sterile water
- further dilute with sterile water or other compatible fluid to a total volume of 1.5 mL = 1000 IU/mL
- Instructions:
- inject 0.2 mL in 5 sites around edge of extravasation site
- administer in conjunction with saline wash out (above)
Washout procedure
Planning for the procedure is critical to ensure success
Consider
analgesia and
sedation requirements, or the need for general anaesthesia.
The procedure should be performed as soon as practical and within 12 hours of the injury meeting treatment requirements (see “Management based on severity” table above)
To perform a washout procedure:
- Ensure adequate
analgesia and
sedation, eg
- 1% lignocaine (max 4 mg/kg) subcutaneously around zone of extravasation or local nerve block. Avoid local anaesthetic with adrenaline
- Intranasal fentanyl or ketamine
- Inhaled nitrous oxide
- IV/IM ketamine
- General anaesthesia
- Use an aseptic technique and clean site with appropriate antiseptic
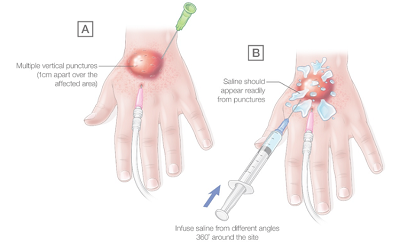
- Use 25G needle to make multiple vertical punctures 1 cm apart around and over the affected area (see figure below)
- Us 23G needle horizontal to skin, infuse 0.9% sodium chloride into the subcutaneous tissue from different angles around the site (360˚°). Infuse at least 2-3 times the estimated extravasated volume
- Infused saline should appear out of the vertical punctures made prior, flushing can be aided by gentle milking of the saline out of these exit points
- Cover the wound with a sterile non-stick dressing, review at least 6 hourly for at least the first 24 hours
- Keep limb warm and elevated for at least 24 hours
Post-procedure care and discharge instructions
- Consider ongoing analgesia requirements
- Daily review by medical staff
- If the line was placed by a consulting team, inform them of the event
- Report to local incident management system
Consider consultation with local paediatric team
- For all children with an extravasation injury
Consider consultation with plastic or relevant surgical team for
- All children with compromise to neurovascular status of the limb or if any concern for compartment syndrome
- All extravasation of medications on the “red infusate” list
- All extravasation injuries with swelling ≥30%
Consider transfer when
- Child requiring care above the level of comfort of the local hospital
- Injury requiring surgical intervention, if not available locally
For emergency advice and paediatric or neonatal ICU transfers, see
Retrieval Services
Parent information
Kids Health Information
Wound care resource
Last updated December 2023