Hypoglycaemia management for insulin injections
Click here for hypo management when using an insulin pump
Hypoglycaemia (“Hypo”) means there is a low level of glucose in the blood
This is a blood glucose value of less than 4.0 mmol/L
Some cause of hypoglycaemia are:
- Too much insulin
- Vigorous exercise without extra carbohydrate
- Missing or delayed meals
- Not eating all serves of carbohydrate
- Alcohol intake
The aim of hypo treatment is to return the blood glucose levels back to target range between 4.0 mmol/L and 7.0 mmol/L
Common signs and symptoms of hypoglycaemia are:
- Paleness
- Shakiness
- Headache
- Sweating
- Feeling hungry
- Dizziness
- Heart pounding
- Irritability, change in mood
- Lack of concentration
- Confusion, vaguenss
- Crying
- weakness
If the BGL is less than 4.0 mmol/L and there are no signs and symptoms, this is still considered hypoglycaemia and requires treatment
Mild hypoglycaemia is common, treatable and to be expected in diabetes management.
Key things to remember when treating a hypo:
- It is important to not over treat hypoglycaemia as will result in a rise of BGLs above 7.0 mmol/L
- Hypo treatment should be taken to the person having the hypo
A blood glucose check should be done to
confirm hypoglycaemia before treating. Treat the hypo if the blood glucose level is less than 4.0 mmol/L. Do not delay treatment.
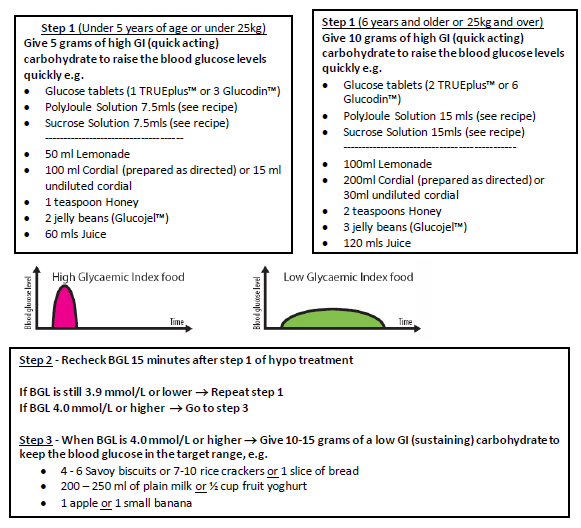
If hypoglycaemia occurs immediately before a meal or snack
- Give the high GI (quick acting) carbohydrate (Step 1), wait 15 minutes until feeling better. It is recommended to recheck the BGL to ensure it is 4.0 or higher.
- If insulin is due, ensure BGL 4.0 mmol/L or higher, give usual insulin dose and serve the meal immediately.