Introduction
A medication administered into subcutaneous tissues is known as a subcutaneous (SC) injection. SC administration is the preferred route for medications requiring slow, steady absorption (given reduced blood supply to adipose tissue).
SC medication administration is a common route of administration of medications in both the hospital and community settings. SC infusion of medications is used widely in palliative care to optimise the delivery of medications and provide appropriate symptom
management, in those patients who have poor gut absorption, nausea, and vomiting. Other patients with acute symptomology could benefit from the SC route of medication administration. Indwelling subcutaneous catheter devices may assist in medication
delivery and decrease trauma, distress, and discomfort for the patient.
Aim
- Facilitate the administration of subcutaneous injections and insertion.
- Manage and remove subcutaneous devices to maximise the therapeutic effect while reducing potential complications and patient discomfort.
Definition of terms
- Subcutaneous:
Between the skin and muscle, the skin, the innermost (deepest) layer of skin.
- Continuous
infusion: A background infusion of medications that is given over a specific period, for example over 24 hours.
- Bolus/breakthrough
dose: A regular or PRN medication that is administered to reduce symptoms. If the patient has a continuous subcutaneous infusion via a BD Saf-T-Intima™, breakthrough subcutaneous medications should be administered via a second BD Saf-T-Intima™.
- BD
Saf-T-Intima™: a SC device used to administer medications in the SC tissue commonly used in patients receiving palliative care
Assessment
Clinical judgement is required when selecting an injection site and needle length. The indwelling subcutaneous catheter device must be inserted into an area where there is adequate subcutaneous tissue.
Site
selection and land marking
Anterior abdominal wall
The anterior abdominal wall is the preferred SC site for children above 2 years old. The recommended volume is 1.5mLs, however larger volumes of 3mLs are well tolerated when injected into the abdominal wall. These areas have a large surface area that
allow rotation for SC injections within the same site for example when administrating clexane™. This site can also be used to insert an indwelling device.
[Picture coming soon]
To landmark the anterior abdominal wall, position the patient lying down or being held by a parent (Procedure Management Guideline). From below the
costal margin to the iliac crest and more than 5cms from the umbilicus. Gently grasp the area to make sure you can pinch 2-5cm of skin.
Anterior upper arm
For children 12 months and older. Use the adipose tissue over the back part of the upper arm. The recommended maximum volume for single injection is 1.5mLs, larger volumes can be associated with pain in this area.
[Picture coming soon]
To landmark this site, the patient should be sitting comfortably, in young children they can be hugging their parent with the back of their upper arm visible. The injection should be given in the outer lateral aspect of the upper arm at least 8cm below
the shoulder and 8cm above the elbow. Gently grasp the area to make sure you can pinch 2-5cm of skin.
Anterior upper thigh
The anterior upper thigh is the preferred SC site for children below 2 years old. The recommended volume is 1.5mLs. This area can have an increased association of pain. Use the front, outer top of the thigh and locate the middle where there is a lot of
adipose tissue. Do not use the inner or back of the thigh. This site can also be used to insert an indwelling device in each thigh if required to rotate medications.
[Picture coming soon]
To landmark this site, the patient should be positioned either laying on their back or held by a parent in a semi-reclined/ relaxed seated position. The injection should be given halfway between the knee and hip slightly to the side. Gently grasp the
area to make sure you can pinch 1-2 inches of skin.
Areas to avoid
- Skin folds or areas where clothing may rub or constrict the flow of medication (particularly in the indwelling subcutaneous device).
- Skin that is edematous, bruised, hard, red, broken or where there is infection.
- Directly over a tumor or areas that have recently been irritated or irradiated.
- Over a bony area or joint.
Special considerations
- The age/developmental needs of the child: for example, do not insert the device in the lower abdomen if the child is in nappies.
- The person who will administer the medication: for example, if the patient is to self-administer, position the hub of the Insuflon™, BD Saf-T-Intima™ or Neria™ Soft device for ease of access for the patient.
- Patient and/or caregiver preference.
- For neonates receiving anticoagulant medications consideration should be given to the appropriateness of using an indwelling device versus rotating injection sites: for example, the administration of Clexane™. In some cases, two indwelling devices
may need to be inserted.
Subcutaneous injection
Needle size
A hypodermic needle is used to administer SC injections.
Needle sizes most commonly used at RCH include:
- 25g x 16mm ORANGE
- 27g x 13mm GREY
Equipment
- Appropriate size needle or device for administration
- Drawing up needle and syringe (if medication not pre-filled)
- Sharps container
- Alcohol impregnated swab (if area visibly soiled)
- Cotton ball
- Band-Aid/small dressing (check for allergies)
- Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) such as gloves for hazardous medications
Procedure
- Prepare patient and obtain consent.
- Perform hand hygiene.
- Prepare equipment as per Aseptic Technique. Open procedure pack or tray or field protecting all key parts.
- Complete the six rights of medication administration.
- Perform hand hygiene. Don PPE if required (particularly for hazardous medications)
- Draw up or prime medication as per Paediatric Injectable
Guidelines
- Position patient in a safe and comfortable position Procedure Management
Guideline
- Consider the use of comfort techniques such as local anesthetic cream and transparent occlusive dressing, cool sense pain numbing applicator, distraction, buzzy bee, ice, or a countdown.
- Landmark injection site (see above)
- Clean site with an alcohol swab (if required)
- Gently grasp the skin to make sure you can pinch 1-2 inches with the non-dominant hand.
- Inject at a 45° angle.
- Release the skin.
- Inject the medication at a slow and steady pace.
- Wait 10 seconds before removing the needle.
- Remove the needle and apply a cotton ball. Remove gloves if worn and perform hand hygiene.
- Place the needle in a sharp container.
- Apply Band-Aid/small dressing if required.
- Perform hand hygiene.
- Clean surfaces, dispose of waste and perform hand hygiene.
- Document procedure on EMR as relevant.
Deep
Subcutaneous
Some medications require administration into the deep subcutaneous tissue as per manufacture instructions. In most cases, these medications come in pre-filled syringes. As with SC injections, positioning and analgesia should be considered prior to use.
Deep SC injections can either be given in the abdomen or upper buttock. In children, the upper buttock is the preferred site as children can be positioned lying on their stomach for comfort and safety. The medication is delivered into deeper tissue
and can be more painful for the child. An order for local anaesthetic such as Lignocaine 1%, can be considered prior to deep SC administration for patient comfort.
Procedure
- Steps 1-11 of procedure (as above)
- Inject the needle halfway at a 45-degree angle.
- Then lower the needle so that it is flat against the skin (180-degree angle) and insert the needle fully so that the hub is against the skin.
- Inject the medication at a slower and steady pace. With some pre-filled medications (e.g., Zoladex™) you will hear the device click and the needle with automatically retract.
- Steps 15-19 of procedure (as above)
[Picture coming soon]
Subcutaneous Device Injection Procedure
Device selection
Indwelling devices: Devices commonly used at RCH include:
|
Insuflon™
|
BD Saf-T-Intima™
|
Neria ™Soft
|
![]() ![]()
![]() Photo taken by RCH staff member Photo taken by RCH staff member
|

Photo taken by RCH staff member
|
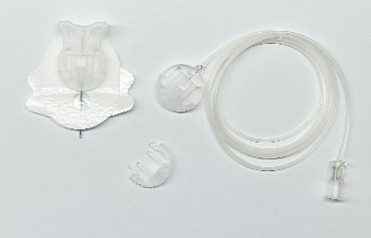
Photo taken by RCH staff member
|
|
The catheter system requires a needle and syringe to administer the medication through the device.
Medications used commonly for daily, or BD dosing include anti-coagulant therapy, chemotherapy an granulocyte colony stimulating factor (GCSF).
|
Used mostly in palliative care patients.
Needless closed indwelling subcutaneous catheter system, which is used for SC administration of medications, either as a continuous infusion or for breakthrough/ bolus doses.
Medications commonly administered via a BD Saf-T-Intima™ can include opioids, benzodiazepines, and anti-emetics.
This device can be attached to a Niki T 34™ syringe driver either on Alaris Asena GH MK III™ for inpatient use, or a Niki T 34™ infusion pump, either for inpatient or outpatient use.
|
Indwelling subcutaneous catheter system which is used for SC administration of medications as an infusion.
Medications administered via a Neria™Soft can include immunoglobin and desferrioxamine (Desderal™). These devices are used in day medical unit by haematology and immunology.
The device features a disconnection option where the indwelling device can remain in situ and the infusion set is attached as required for medication administration.
The device is often used for subcutaneous infusions of short duration and attached to a syringe driver such as a Niki T 34™ infusion pump or a Springfusor™ syringe infusion pump.
|
Equipment
- SC device and supplied dressing or transparent occlusive dressing if required.
- Red caps (if required)
- Alcohol wipes
- Sharps container
Procedure
Follow steps 1-13 of SC procedure (as above)
|
Insuflon™
|
BD Saf-T-Intima™
|
Neria ™Soft
|
- Clean site with an alcohol swab (if required)
- Hold the Insuflon™ catheter hub between the thumb and index finger and remove the cap.
- With the bevel up, insert the Insuflon™ into subcutaneous tissue, advancing the total length of the catheter at a 20° to 45° angle to the skin surface.
- Holding the catheter hub firmly, remove the needle by pulling it out slowly, leaving the catheter in place.
- Dispose of the needle in a sharp’s container
- Secure the Insuflon™ by applying the dressing supplied from the catheter end first, ensuring the insertion site is visible and the hub is not covered.
|
- Remove the white clamp from the BD Saf-T-Intima™ (prevents clamping)
- Remove the flow control plug from the Y injection port to prime the system, flush the BD Saf-T-Intima™ with at least 0.3 mls of water for injection (WFI) to ensure patency.
- Clean site with an alcohol swab (if required)
- Remove needle cover and inspect unit.
- Holding the catheter, rotate the safety barrier to loosen the needle.
- Ensure the bevel is not covered by the catheter; hold the pebbled sides of flange to ensure they are in contact with the skin surface when the catheter is inserted.
- Grasp the skin at the site of insertion. You may need assistance to stabilise the insertion site.
- With the bevel facing up insert the BD Saf-T-Intima™ into the SC tissue, advancing the total length of the catheter at a 20° to 45° angle to the skin surface.
- Release wings and stabilise with a transparent occlusive dressing.
- Place a small amount of pressure on the wings to ensure the catheter does not become dislodged and grasp the white needle shield. Pull back slightly to recess the introducer needle. The white needle shield will be removed, exposing
the infusion port with a plastic adapter insitu.
- Remove the plastic adapter (this is not required) from the infusion port of the straight arm of the BD Saf-T-Intima™.
- If an infusion is being commenced, connect the infusion directly to the straight arm of the BD Saf-T-Intima™ and a red cap on the Y injection port.
- If the BD Saf-T-Intima™ is being used for breakthrough doses place a red cap on both infusion/ injection ports.
- DO NOT attach a smart site. If using for an infusion the battery cannot push past the smart site and will occlude the infusion.
|
- Remove the front part of the adhesive backing and gently remove the needle guard from the Neria ™Soft device.
- Clean site with an alcohol swab (if required)
- Grasp the skin at the site of insertion. You may need assistance to stabilise the insertion site.
- Ensure the bevel is up, insert the Neria ™Soft into the subcutaneous tissue, advancing the total length of the catheter at a 90° angle to the skin surface.
- Remove the introducer needle by holding the catheter hub firmly; while pinching the sides of the plastic introducer together, pull the needle out slowly, leaving the catheter in place.
- Remove the remaining adhesive.
paper. Press the adhesive onto
the skin to secure the device.
The connector hub will be open.
to air.
- If an infusion is being commenced, insert the connector needle of the infusion tubing directly to the Neria ™Soft. If an infusion is not be commenced, connect supplied
plastic guard to the Neria ™Soft
device
|
-
Dispose of needle in a sharp’s container.
- Write date of insertion on the dressing.
- Insertion of the indwelling SC catheter device and site should be clearly documented in the EMR. The insertion should be recorded in the LDA (Lines, Drains, Airways) flowsheet and the avatar.
Subcutaneous Device Management
- Observe the SC device and insertion site once daily and prior to medication administration including bolus/breakthrough doses.
- Devices which are being used to administer continuous infusions should be observed at least four hourly as well as prior to bolus/breakthrough doses of medication
- S/C devices need to be changed at regular intervals, please see the table below for recommendations on commonly used devices at RCH. Please note this table is a guide only and devices may need to be changed more frequently due to the use of some medications*
or if complications occur.
|
Device
|
Reinsertion interval
|
Additional considerations
|
|
Insuflon™
|
7-10 days
|
- Two Insuflons™ should be used if:
- The patient is on a daily dose (to rotate the site)
- Smaller infants receiving Clexane™ to minimise significant bruising.
- Patients having 2 different medications that cannot be given via the same device.
- The two Insuflon™ devices should be placed in different areas, for example on a different limb or alternatively opposite sides of the abdomen.
|
|
BD Saf-T-Intima™
|
Up to 14 days
|
- Two BD Saf-T-Intima™ devices should be used if the patient requires a continuous infusion as well as breakthrough medication
- Never use the infusion line to give breakthrough/bolus doses of medication
- The two devices should be placed in different areas
|
|
Neria ™Soft
|
After 12 hours of use with immunoglobins and apomorphine
After 72 hours of use with hydromorphone, morphine sulphate and morphine chloride
|
- Take care to not pull the cannula housing out of the insertion handle.
- Ensure there is no gap between the cannula housing and the insertion handle.
- Tubing can be disconnected at the site
|
*Some medications may increase the need for more frequent catheter changes, as examples
- Low molecular weight heparin (ClexaneTM) – may increase bruising or bleeding at the site
- Ketamine- may cause redness and irritation at the site more quickly than other medications
- Insulin- may contribute to the breakdown of adipose tissue at the site
|
Management of complications
Poor technique and incorrect site selection of the injection site can lead to site reactions, sub-optimal medication absorption and adverse events.
Potential complications:
- Infection
- Discomfort
- Difficulty injecting medication
- Blockage
- Redness
- Inflammation
- Exudates
- Bruising and bleeding
- Pain
- Leakage
Management
- Do not reinsert the needle if the catheter is dislodged/ withdrawn, instead repeat insertion with a new SC device.
- Never reinsert the needle into the catheter as this could shear the catheter.
- Do not bend the needle prior to insertion.
- Complications should be documented in the LDA or Progress Notes
- Consider need to notify the medical team of complications i.e., Excessive bruising/bleeding when Clexane™ is being administered
- In patients who have a BD Saf-T-Intima™ insitu, consider dexamethasone addition to preserve sites ongoing. Discuss with VPPCP (Victorian Paediatric Palliative Care Program).
Administration of medication via a subcutaneous device
Ensure all medications given are recommended for subcutaneous use. Medications are ordered on the MAR and administered as per the Medication
Management Procedure
Equipment
- Appropriately sized syringe
- Drawing up needle
- Luer lock syringe
- Red caps
- 75 cm minimum volume extension set (if using for continuous infusion)
- Alcohol swab
- Sharps container
|
Device
|
Administration
|
Flushing
|
Other Considerations
|
|
Insuflon™
|
Follow Steps 1-7 in the above S/C procedure
- Clean the hub/ injection port of the S/C device with an alcohol wipe and allow to dry
- Insert the needle fully into the Insuflon™ hub or connect syringe to the Insuflon™ injection port
- Administer the medication as ordered
- Observe the insertion site whilst administering medication (look for signs of blanching or redness as it may indicate that site is no longer appropriate for S/C medications)
- Remove the needle and syringe post administration of medication
- Replace red cap on the Insuflon™ injection port
- Dispose of needle and syringe in the sharp’s container
- Document on the MAR as appropriate
- Consider rotating between 2 insitu insuflons when administering clexane.
|
approximately 0.0075 ml
- Flush not required before or after use.
|
Some medications may cause pain at the site whilst injecting (e.g., GCSF and Clexane™)
- 1. Apply ice to the site for 5 minutes prior to injecting the medication
- 2. Utilise distraction techniques
- 3. Gently rub/tickle the site during medication administration
- 4. Apply pressure with the fingertips to the distal tip on the implanted catheter for 2-5 minutes (this reduces bruising at the site and is particularly important when administering clexane via an insuflon)
- Removal of the device should only occur 15-30mins post last medication administration
|
|
BD Saf-T-Intima™
|
Please note that in some instances it will take approximately 30 minutes for the medication to reach the patient; give a bolus/breakthrough dose of medication prior to commencing the infusion.
Continuous infusions
Follow Steps 1-3 as above
- For continuous infusions attach and prime the luer lock syringe to the minimum volume extension set
- Clean the infusion port on the straight arm of the BD Saf-T-Intima™ with an alcohol wipe and allow to dry
- Attach a primed minimum volume extension line to the infusion port on the straight arm of the BD Saf-T-Intima™.
- Ensure there is a red cap on the Y injection port of the BD Saf-T-Intima™
- Follow steps 5- 9 as above.
|
- Dead space volume: approximately 0.25 ml
- Flush required after the administration of bolus/breakthrough doses.
- Ensure flush used is compatible with the medication (see below)
|
- Continuous infusion lines should be changed every 3 days or when the concentration of the medication changes.
- More than one medication can be used in a continuous infusion syringe, check medication compatibilities.
- Do not use smart sites on the ends of the infusion ports.
- When using for continuous infusion, connect the minimum volume extension line directly to the straight arm of the BD Saf-T-Intima™
- Place a red cap on the Y injection port
- Do not administer breakthrough/ bolus doses via the straight arm once an infusion has commenced.
|
|
Neria™ Soft
|
Disconnecting the tubing:
- Perform hand hygiene and stop the infusion
- Place a finger in front of the cannula housing and gently squeeze the sides of the connector. Pull the connector straight out from the cannula housing
- Place the white disconnect cover (tubing) on the connector
Reconnecting the tubing:
- Perform hand hygiene
- Remove the canula housing by placing a finger in front of the cannula housing and gently squeeze the sides of the disconnect cover. Pull the disconnect cover straight out of the cannula housing
- Prime the tubing.
- Place a finger in front of the cannula housing and push the connector straight in until it clicks.
|
- Flushing not required
- Priming volumes of tubing:
30cm tubing: 0.05ml
60cm tubing: 0.10ml
110cm tubing: 0.18 ml
|
|
Drug Compatibility Guidelines
Please follow the link below for a comprehensive list of drug compatibility used in a subcutaneous infusion.
https://www.safercare.vic.gov.au/sites/default/files/2021-02/GUIDANCE_Syringe%20driver%20compatability%20FINAL_0.pdf
Removal of a subcutaneous device
Equipment
- Band-Aid or transparent occlusive dressing
- Gauze/ cottonwool
Procedure
- Perform the five moments of hand hygiene.
- Explain the procedure to the child (if appropriate) and parents/ caregivers.
- Utilise standard aseptic technique Aseptic Technique
- Remove the dressing from the skin, it may be helpful to place a small amount of pressure on the device/ wings of the S/C device as you remove the dressing.
- Withdraw the S/C device from the insertion site in one quick, smooth movement.
- Apply gauze over the insertion site (if required)
- Apply a transparent occlusive dressing. If there is an increased amount of exudate from the site, an absorbent dressing can be used.
- Dispose of any waste in the appropriate bins
- Perform hand hygiene.
- Complete appropriate documentation. Removal of the device should be documented in the LDA flowsheet and the avatar.
Companion Documents
Evidence Table
| Reference
|
Source of Evidence |
Key
findings and considerations |
| Canberra Hospital and Health Services (2017). Clinical Procedure Manual – Subcutaneous Medication management in the Care of the Palliative Patient – Adult Only. Australia: Canberra Hospital & Health Services. https://starship.org.nz/guidelines/continuous-infusions-in-paediatric-palliative-care-using-a-nikit34-syringe |
Clinical Practice Guideline
|
Main indications of use of indwelling subcutaneous device BD Sat-T-Intima · Insertion sites · Procedure for use · Preparing medication and infusion for NikiT34
|
Government of Western Australia Child and Adolescent Health Service. (2023, August). Medication administration. Medication Administration .
https://www.cahs.health.wa.gov.au/-/media/HSPs/CAHS/Documents/Health-Professionals/Neonatology-guidelines/Medication-Administration.pdf
|
Clinical Practice Guideline
|
Clinical practice guideline outlining SC procedure of a subcutaneous injection
|
Griffin, K. (2021). Guidelines for subcutaneous infusion in Palliative Care. Guidelines for Subcutaneous Infusion Device Management in Palliative Care and other settings – 3rd Edition. https://www.health.qld.gov.au/__data/assets/pdf_file/0029/155495/guidelines.pdf
|
Clinical Practice Guideline
|
The Niki T34® is commonly used in end of life care across all settings as well as in complex symptom management in other areas of care;
- A Luer-Lok® syringe should be used to prevent risk of disconnection; syringes should be validated for use with the device selected;8 20 ml is the recommended minimum size;9
- An aseptic technique should be used when preparing and setting up the infusion;10 · A minimum volume extension set should be used to minimise dead- space in the line;8
- When changing the extension set and/or cannula, prime the line after drawing up the prescribed medications in the syringe8,11 and document the line change and the time the syringe is calculated to finish;
- A Teflon® or Vialon® cannula, such as the BD Saf-T-Intima®, should be used in preference as they are associated with significantly less risk of site inflammation than metal butterfly needles;
- The longevity of the site can vary considerably from 1–14 days;12
- Select and use sites on a rotating basis;8 · Use of a transparent, semi-occlusive dressing to cover the site is recommended to allow for inspection of the site;10
- Site reactions can be caused by factors including: the tonicity (concentration) of the medication, the pH of the solution, infection, and prolonged presence of a foreign body (the cannula);4
- The site should be inspected regularly for early identification of issues and reduce the risk of site related complications.
- Principals for site preparation · Insertion procedure of the BD Saf-T-Intim
|
| Kroger, A. T., Sumaya, C. V., Pickering, L. K., & Atkinson, W. L. (2011). General recommendations on immunization: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). General Recommendations on Immunization: Recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP). https://www.cahs.health.wa.gov.au/-/media/HSPs/CAHS/Documents/Health-Professionals/Neonatology-guidelines/Medication-Administration.pdf |
|
- Subcutaneous injections are administered at a 45-degree angle, usually into the thigh for infants aged <12 months and in the upper-outer triceps area of persons aged ≥12 months.
- Subcutaneous injections may be administered into the upper-outer triceps area of an infant if necessary.
- A ⅝-inch, 23- to 25-gauge needle should be inserted into the subcutaneous tissue
- Comfort measures, such as distraction (e.g., playing music or pretending to blow away the pain), ingestion of sweet liquids, breastfeeding, cooling of the injection site, and topical analgesia, can help infants or children cope with the discomfort associated with vaccination
|
Shepherd E (2018) Injection technique 2: administering drugs via the subcutaneous route. Nursing Times [online]; 114: 9, 55-57. https://www.nursingtimes.net/clinical-archive/assessment-skills/injection-technique-2-administering-drugs-via-the-subcutaneous-route-28-08-2018/
|
Recommendations from authoritative body |
Landmarking of subcutaneous injections - Lifted skin hold technique
- Needle size used
- Equipment used
- Procedure used
- Angle of injections
- Medication administration
|
| WHO best practices for injections and related procedures toolkit - 2010 |
Recommendations from authoritative body |
When using a sterile single-use device (i.e. a syringe and hypodermic needle that is not separated or manipulated unless necessary:
- use a new device for each procedure, including for the reconstitution of a unit of medication or vaccine;
- inspect the packaging of the device to ensure that the protective barrier has not been breached;
- discard the device if the package has been punctured, torn or damaged by exposure to moisture, or if the expiry date has passed.
|
| https://www.neria.com/about-neria/neria-product-range/neria-guard/ | Manufacture information | Neria product manufacture information |
https://www.bd.com/en-ca/products-and-solutions/products/product-families/bd-saf-t-intima-closed-iv-catheter-system
|
Manufacture information
|
BD Saf-T-Intima manufacture information
|
| https://www.convatec.com/products/infusion-care/product-type/pc-type-injection-port/315ca64f-8f47-4a21-8b08-bc4292573138/ |
Manufacture information |
Insuflon manufacture information
|
Please remember to read the
disclaimer.
The revision of this nursing guideline was coordinated by Natalie Tingate, RN, Kookaburra, and approved by the Nursing Clinical Effectiveness Committee. Updated April 2024.